
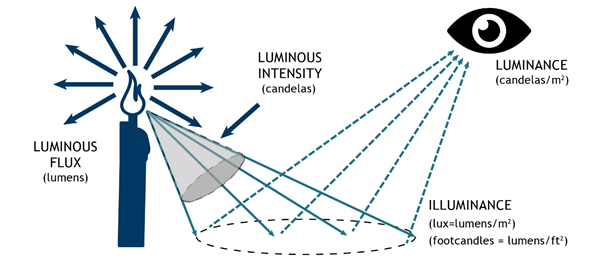
Integrating spheres reflect obtained optical signals around an internalĬavity into a sensitive detector. However is the most compact and thus most practical solution.ġ80° field of view with a Lambertian response and diffuse it, while Luminous intensity measurements must be equipped with either a cosineĬorrector or an integrating sphere in 2π configuration. Measurement instrumentation is commonly used toĪcquire multiple photometric measurements to assess the broad opticalĬharacteristics of a light source. Intensity measurements are carried out in isolation without interference Measurement Instruments for Luminous Intensity Quality control of commercial LEDs and SSL. Sensitivity is a critical process for development, manufacture, and Optical output of a directional light source against an averaged human Lighting (SSL) for domestic and commercial spotlights. Measuring high-power light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and solid-state Luminous intensity is particularly important for The latter of which refers to the optical power output in a definedįield of view. Measures the power output according to Vλ of a light source in allĭirections, and is expressed in lumens (lm).ĭifference between luminous flux and luminous intensity – Intensity of a light source is distinct from its luminous flux, which It is expressed as a unit of candela (cd)Īnd is measured according to the Vλ luminosity function. Luminous intensity in further detail, and explore some of theĪppropriate light measurement instruments for assessing the intensity ofĪs brightness, is the quantity of wavelength-weighted power of a lightĮmitted per unit solid-angle. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the luminous efficacy of monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 x 10 12 Hz, K cd, to be 683 when expressed in the unit lm W -1, which is equal to cd sr W -1, or cd sr kg -1 m -2 s 3, where the kilogram, meter and second are defined in terms of h, c and Δ ν Cs.Photometric measurements are concerned with the luminous power (lm), illuminance (lm/m 2 or lux), luminance (cd/m 2), and luminous intensity (cd) of a light source. The candela, symbol cd, is the SI unit of luminous intensity in a given direction. An elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an electron, any other particle or specified group of particles. The amount of substance, symbol n, of a system is a measure of the number of specified elementary entities. This number is the fixed numerical value of the Avogadro constant, N A, when expressed in the unit mol -1 and is called the Avogadro number. One mole contains exactly 6.022 140 76 x 10 23 elementary entities. The mole, symbol mol, is the SI unit of amount of substance.

It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Boltzmann constant k to be 1.380 649 x 10 -23 when expressed in the unit J K -1, which is equal to kg m 2 s -2 K -1, where the kilogram, meter and second are defined in terms of h, c and Δ ν Cs. The kelvin, symbol K, is the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1.602 176 634 x 10 -19 when expressed in the unit C, which is equal to A s, where the second is defined in terms of Δ ν Cs. The ampere, symbol A, is the SI unit of electric current. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the cesium frequency Δ ν Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the cesium 133 atom, to be 9 192 631 770 when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s -1. The second, symbol s, is the SI unit of time. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Planck constant h to be 6.626 070 15 × 10 -34 when expressed in the unit J s, which is equal to kg m 2 s -1, where the meter and the second are defined in terms of The kilogram, symbol kg, is the SI unit of mass. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the speed of light in vacuum c to be 299 792 458 when expressed in the unit m s -1, where the second is defined in terms of
The meter, symbol m, is the SI unit of length. The following seven SI base unit definitions are based on the BIPM SI Brochure (9th Edition). Become familiar with the seven defining constants of the SI.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
